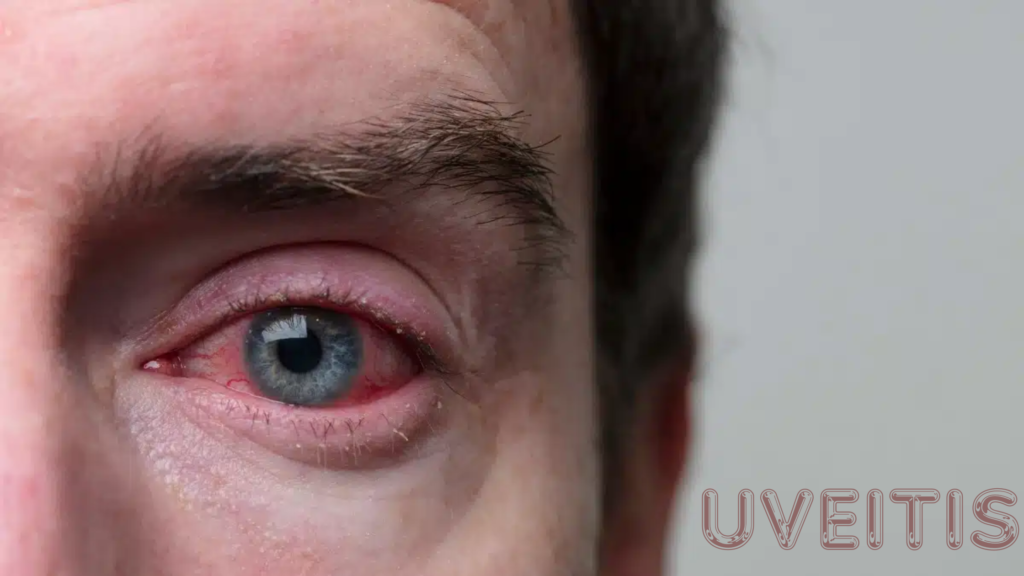
👁️ Uveitis – Overview
Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye that includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. It can cause eye pain, redness, and vision problems, and may lead to serious complications if untreated.
⚙️ Types of Uveitis
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Anterior uveitis (iritis) | Most common; affects the front part of the eye (iris) |
| Intermediate uveitis | Inflammation of the ciliary body and vitreous |
| Posterior uveitis | Affects the back part of the eye (choroid and retina) |
| Panuveitis | Inflammation of all parts of the uvea |
📋 Symptoms
- Eye redness
- Eye pain or aching
- Light sensitivity (photophobia)
- Blurred vision or decreased vision
- Floaters (spots in vision)
- Sometimes headache
⚙️ Causes
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis)
- Infections (e.g., herpes, tuberculosis, syphilis)
- Eye injury or trauma
- Unknown (idiopathic)
🩺 Diagnosis
- Eye exam including slit-lamp microscopy
- Measuring intraocular pressure
- Blood tests and imaging to find underlying causes
- Eye ultrasound or fluorescein angiography if needed
💊 Treatment
- Corticosteroid eye drops to reduce inflammation
- Oral steroids or immunosuppressive drugs for severe cases
- Treatment of underlying infection if present
- Dilating eye drops to reduce pain and prevent complications
⚠️ Complications
- Glaucoma
- Cataracts
- Retinal swelling or detachment
- Permanent vision loss if untreated
🛡️ Prevention & Management
- Regular eye exams if at risk
- Prompt treatment of symptoms
- Managing systemic diseases that cause uveitis