Ureteropelvic Junction (UPJ)
The ureteropelvic junction is the area where the renal pelvis (the funnel-shaped part of the kidney that collects urine) meets the ureter, the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder.
📌 Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJO)
UPJO is a condition where there is a narrowing or blockage at the UPJ, which restricts the flow of urine from the renal pelvis into the ureter. This can lead to hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney) and potential kidney damage over time.
🧬 Causes
1. Congenital (most common, especially in children)
- Incomplete development of the muscular wall at the UPJ.
- Abnormal blood vessels crossing the junction and compressing it.
- Narrowed segment present from birth.
2. Acquired (seen in adults)
- Kidney stones
- Scar tissue from surgery or infection
- Tumors
- External compression (e.g., from blood vessels or masses)
⚠️ Symptoms
- Flank or abdominal pain, especially after drinking lots of fluids (due to increased urine flow)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Hematuria (blood in the urine)
- In infants: palpable abdominal mass, poor feeding, or failure to thrive
- In some cases: asymptomatic, found incidentally
🧪 Diagnosis
- Ultrasound – Shows hydronephrosis (dilated renal pelvis and calyces).
- Diuretic renal scan (MAG3 or DTPA) – Measures urine drainage and differential kidney function.
- CT or MRI urogram – Provides detailed anatomy and can identify crossing vessels.
- Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) – Rules out vesicoureteral reflux in children.
🩺 Treatment
Observation (if mild and kidney function is preserved)
- Regular imaging and renal function monitoring.
Surgical intervention (if symptomatic or functional impairment)
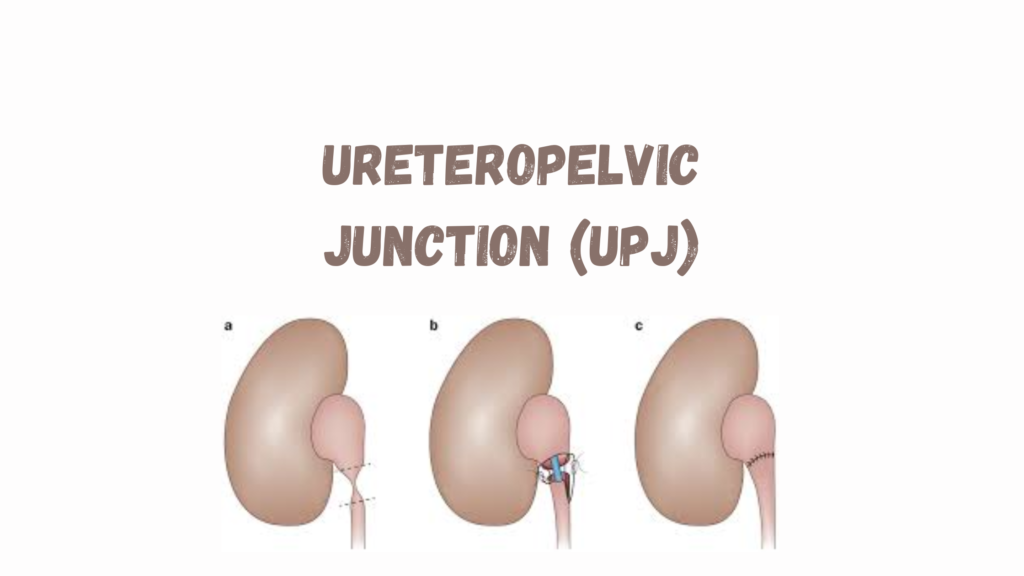
- Pyeloplasty (standard treatment): Surgical removal of the obstructed segment with reconnection to a healthy ureter.
- Open, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted
- Endopyelotomy: Minimally invasive cutting of the narrowed segment via a scope (less commonly done now).
- Temporary drainage with:
- Ureteral stent
- Percutaneous nephrostomy tube
✅ Prognosis
- Excellent with proper treatment, especially in children.
- Most patients retain or regain normal kidney function post-pyeloplasty.