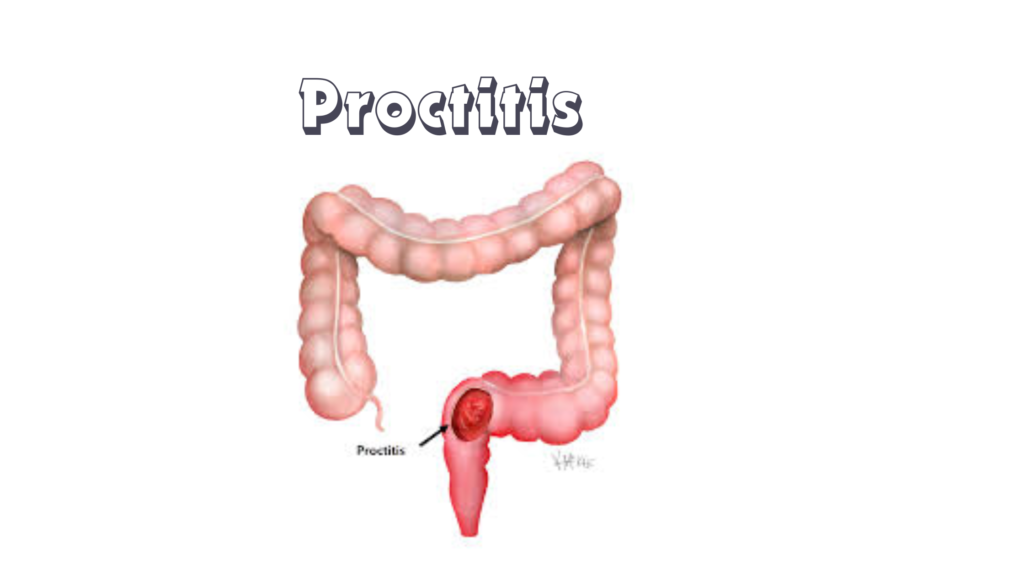
Proctitis is inflammation of the rectal mucosa, the lining of the last few inches of the large intestine (rectum). It causes discomfort and symptoms related to irritation of the rectum.
📚 Causes of Proctitis
1. Infectious Proctitis
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs):
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Chlamydia trachomatis (including Lymphogranuloma venereum)
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
- Treponema pallidum (syphilis)
- Enteric pathogens:
- Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter
- C. difficile (especially after antibiotic use)
2. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Ulcerative colitis (limited to rectum: proctitis)
- Crohn’s disease
3. Radiation Proctitis
- Due to pelvic radiation therapy for cancers (e.g., prostate, cervical)
4. Ischemic Proctitis
- Reduced blood flow to rectum (rare)
5. Chemical or Trauma
- Enemas, rectal trauma, or insertion of foreign objects
😖 Symptoms
- Rectal pain and discomfort
- Urgency and tenesmus (feeling of incomplete evacuation)
- Rectal bleeding or mucous discharge
- Diarrhea or constipation
- In severe cases: fever, abdominal pain
🔍 Diagnosis
- History and physical exam, including digital rectal exam
- Anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy: visualize inflamed mucosa, ulcers, or erosions
- Stool tests: culture, PCR for infections
- Biopsy (if needed) to rule out IBD or malignancy
- Imaging if complications suspected
💊 Treatment
🔹 Infectious Proctitis
- Targeted antibiotics or antivirals based on pathogen:
- Gonorrhea: Ceftriaxone
- Chlamydia: Doxycycline or azithromycin
- Herpes: Acyclovir
- Syphilis: Penicillin G
🔹 IBD-related Proctitis
- Mesalamine suppositories or enemas
- Corticosteroids for flares
- Immunosuppressants or biologics for severe disease
🔹 Radiation Proctitis
- Symptomatic relief with sucralfate enemas, steroids, or hyperbaric oxygen therapy (severe cases)
🔹 Supportive Care
- Pain management
- Stool softeners to reduce strain
✅ When to See a Doctor
- Persistent rectal bleeding
- Severe pain or systemic symptoms
- Suspected STI exposure
- Symptoms not improving with initial treatment