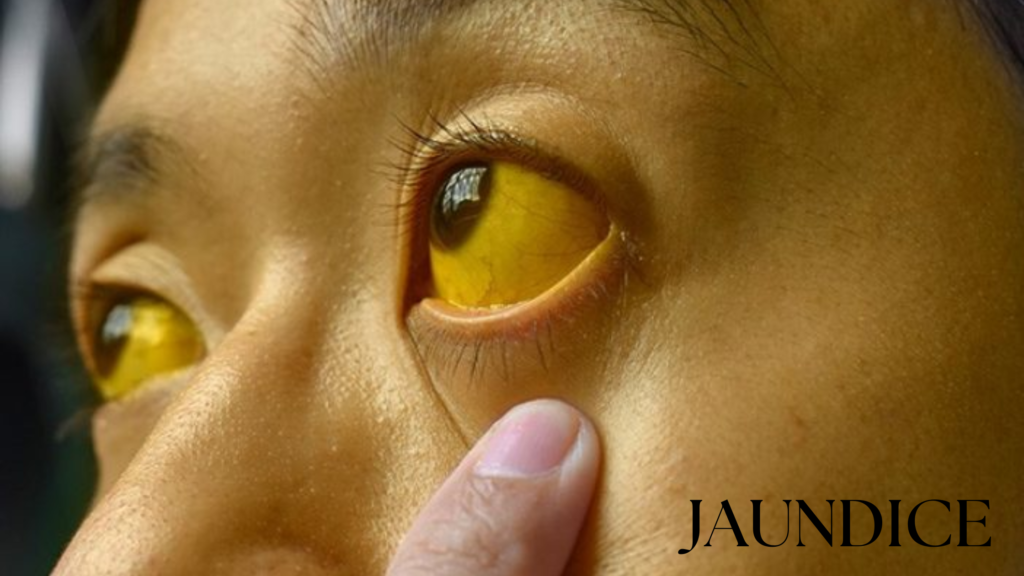
🟡 Jaundice
Jaundice is a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes due to a buildup of bilirubin — a yellow pigment formed by the breakdown of red blood cells.
It is not a disease itself, but a sign of an underlying condition, often related to the liver, bile ducts, or red blood cells.
🧬 What Is Bilirubin?
- A yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- Normally processed by the liver, excreted into bile, and eliminated through stool.
When this process is disrupted, bilirubin builds up in the blood, leading to jaundice.
🩸 Types of Jaundice
| Type | Cause |
|---|---|
| Pre-hepatic | Increased breakdown of red blood cells (e.g. hemolytic anemia) |
| Hepatic | Liver dysfunction (e.g. hepatitis, cirrhosis) |
| Post-hepatic | Blockage of bile flow (e.g. gallstones, tumors, bile duct obstruction) |
⚠️ Common Causes
🔹 In Adults:
- Hepatitis (A, B, C, E)
- Liver cirrhosis
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Gallstones
- Pancreatic or liver cancer
- Hemolytic anemia
- Drug-induced liver injury
🔹 In Newborns:
- Physiological jaundice (common and usually harmless)
- Breast milk jaundice
- Blood group incompatibility (Rh or ABO)
- Liver enzyme immaturity
🩻 Symptoms of Jaundice
- Yellowing of skin and eyes
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Itching (pruritus)
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain (especially in right upper quadrant)
- Nausea or vomiting (in liver-related jaundice)
🧪 Diagnosis
- Physical exam (yellowing of eyes/skin)
- Blood tests:
- Total, direct, and indirect bilirubin
- Liver function tests (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT)
- CBC (anemia or infection)
- Imaging:
- Ultrasound, CT, or MRI of the liver and bile ducts
- Liver biopsy (in complex cases)
💊 Treatment
- Depends on the underlying cause:
- Hepatitis: Supportive care or antivirals
- Gallstones: Surgery or ERCP (endoscopic removal)
- Liver failure: May require transplant
- Hemolysis: Treat underlying blood disorder
In newborns:
- Phototherapy (blue light therapy)
- Exchange transfusion (in severe cases)
🛡️ Prevention
- Vaccination (Hepatitis A & B)
- Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic drugs
- Practice safe sex and hygiene
- Avoid contaminated water/food in endemic areas
- Regular monitoring if you have liver disease
✅ Key Facts
- Jaundice is a symptom, not a disease
- It signals liver or blood-related problems
- Newborn jaundice is common and usually resolves on its own
- Timely diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause are crucial