😷 Herpangina
Herpangina is a viral illness characterized by painful ulcers or sores in the mouth, particularly in the back of the throat, and often accompanied by fever. It most commonly affects children, especially during summer and early fall.
🧬 Cause:
- Caused by enteroviruses, most commonly:
- Coxsackievirus A (especially A6, A10, A16)
- Echoviruses or enterovirus 71 (less often)
🧒 Who Gets It?
- Primarily affects infants and children aged 3–10 years
- Spread by:
- Fecal-oral route
- Respiratory droplets
- Contaminated surfaces (poor hand hygiene)
🩺 Symptoms:
- Sudden high fever
- Sore throat
- Painful swallowing
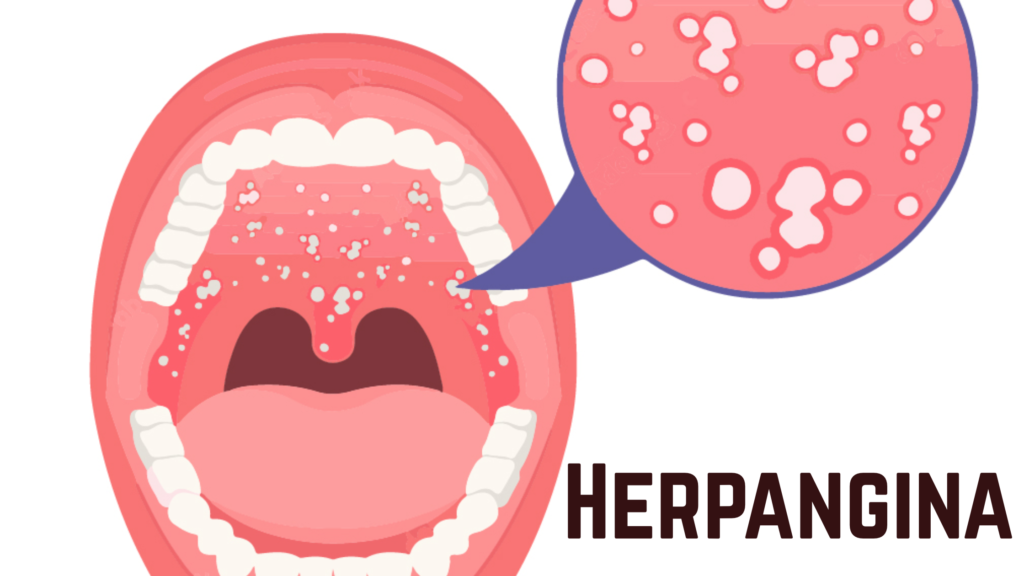
- Tiny red spots in the back of the mouth (soft palate, tonsils, uvula)
- These spots turn into small ulcers with a red border
- Loss of appetite
- Drooling (in infants)
- Headache, abdominal pain, or vomiting (sometimes)
Unlike hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), herpangina usually does not involve a skin rash.
🔍 Diagnosis:
- Clinical diagnosis based on symptoms and appearance of mouth sores
- Lab tests (PCR or viral culture) rarely needed unless severe or unclear
💊 Treatment:
Herpangina is self-limiting and typically resolves in 5–7 days.
- Supportive care:
- Fever and pain relief: acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Hydration: plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration
- Soft, bland foods (avoid spicy or acidic items)
- Cold liquids or ice pops may soothe throat
- Antivirals and antibiotics are not used unless complications arise
⚠️ Complications (rare):
- Dehydration (due to pain and reduced fluid intake)
- Febrile seizures (due to high fever)
- Viral meningitis or encephalitis (extremely rare)