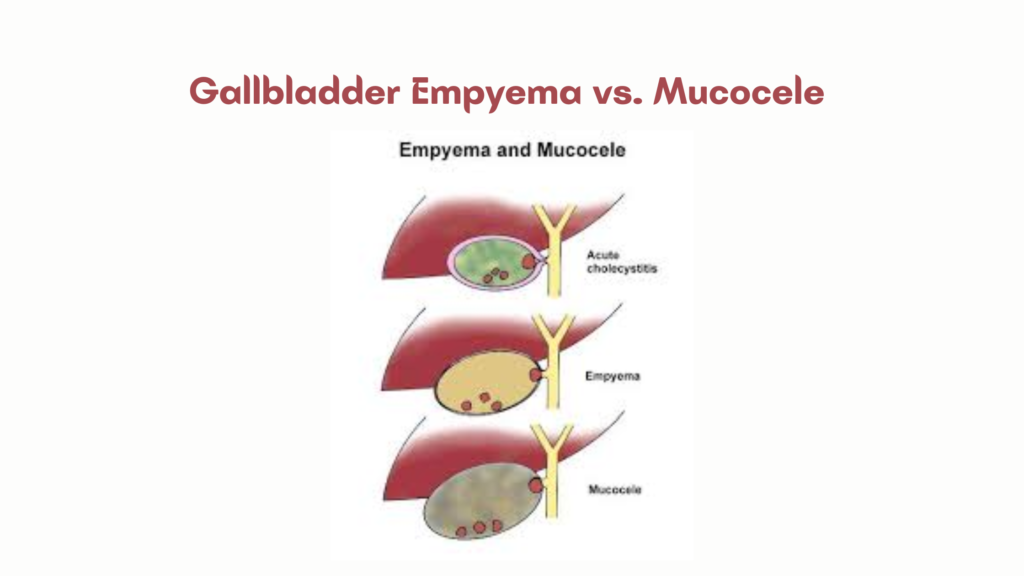
Gallbladder Empyema vs. Mucocele
Both gallbladder empyema and mucocele are complications of gallbladder obstruction, typically related to cholelithiasis (gallstones). However, they differ in severity, contents, and urgency of treatment.
🦠 Gallbladder Empyema
Definition:
A gallbladder empyema is a severe form of acute cholecystitis in which the gallbladder becomes filled with pus, usually due to bacterial infection following cystic duct obstruction.
⚠️ Key Features:
- Pus-filled gallbladder
- Caused by superinfected gallbladder contents
- Often follows acute cholecystitis
- High risk of perforation, sepsis
🧪 Clinical Presentation:
- Severe right upper quadrant pain
- Fever, chills
- Toxic appearance
- Leukocytosis
- Tender, possibly palpable mass in the RUQ
🧬 Common Organisms:
- E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterococcus, Bacteroides
📷 Imaging:
- Ultrasound/CT scan:
- Enlarged gallbladder
- Thickened wall
- Internal echoes (pus)
- Pericholecystic fluid
💊 Management:
- Urgent surgical intervention: Usually cholecystectomy
- If patient unstable: Percutaneous cholecystostomy + IV antibiotics
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics (e.g., pip-tazo, ceftriaxone + metronidazole)
💧 Gallbladder Mucocele
Definition:
A mucocele is a distended, mucus-filled gallbladder, usually due to chronic cystic duct obstruction without infection.
⚠️ Key Features:
- Mucus or clear fluid accumulation (not pus)
- Often asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic
- Sterile contents
- Risk of compression or perforation if untreated
🧪 Clinical Presentation:
- Often incidental finding
- May have vague abdominal discomfort
- No signs of infection (no fever, systemic symptoms)
📷 Imaging:
- Enlarged gallbladder with anechoic contents
- Thin walls
- No signs of inflammation or infection
💊 Management:
- Elective cholecystectomy
- No need for emergency surgery unless complications arise
🔍 Summary Table:
| Feature | Gallbladder Empyema | Gallbladder Mucocele |
|---|---|---|
| Content | Pus | Mucus |
| Cause | Acute cholecystitis + infection | Chronic cystic duct blockage |
| Symptoms | Severe pain, fever, sepsis | Often asymptomatic |
| Treatment urgency | Emergency | Elective |
| Risk if untreated | Perforation, sepsis | Compression, rupture |