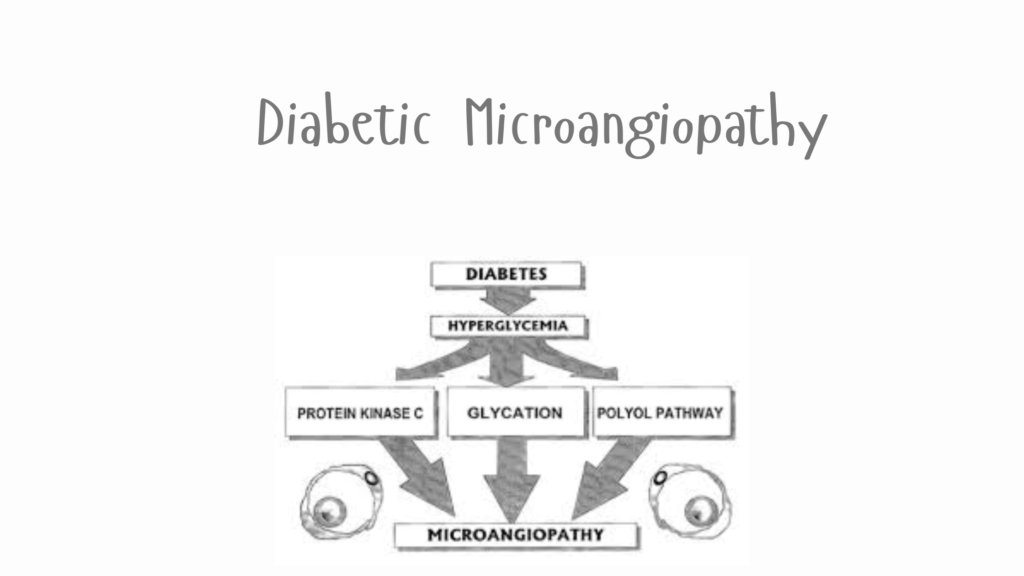
Diabetic Microangiopathy is a complication of diabetes mellitus that affects the small blood vessels (capillaries) throughout the body. It is caused by long-term high blood sugar levels, which damage the walls of these small vessels, leading to thickening, leakage, and reduced blood flow.
🔍 What Happens in Microangiopathy?
- Chronic hyperglycemia (high blood glucose) damages endothelial cells lining capillaries.
- This leads to:
- Basement membrane thickening
- Capillary occlusion
- Impaired oxygen and nutrient delivery
- Tissue ischemia and damage
📌 Key Areas Affected
- Eyes – Diabetic Retinopathy
- Capillary damage in the retina causes microaneurysms, hemorrhages, and potentially blindness.
- Kidneys – Diabetic Nephropathy
- Damage to glomerular capillaries leads to proteinuria, kidney dysfunction, and eventually chronic kidney disease.
- Nerves – Diabetic Neuropathy
- Poor perfusion of nerves causes numbness, tingling, pain, especially in the feet and hands.
⚠️ Symptoms by System
👁️ Eyes (Retinopathy)
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Floaters
- Vision loss (in advanced stages)
🩸 Kidneys (Nephropathy)
- Protein in urine (early sign)
- Swelling (especially around the eyes, ankles)
- High blood pressure
⚡ Nerves (Neuropathy)
- Burning, tingling, or numbness
- Pain or weakness in extremities
- Digestive, urinary, or sexual dysfunction (autonomic neuropathy)
🧪 Diagnosis
- Retinal exams (fundoscopy, OCT, fluorescein angiography)
- Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR)
- Nerve conduction studies
- Blood tests: HbA1c, fasting glucose, eGFR, and creatinine
💊 Treatment
🔧 Glycemic Control
- Tight blood sugar control is the most important preventive measure
- Target HbA1c < 7% (individualized)
💉 Medications
- ACE inhibitors / ARBs (protect kidney function)
- Statins (reduce vascular risk)
- Antiplatelets (in some cases)
- Pain management for neuropathy (e.g., pregabalin, duloxetine)
👟 Lifestyle
- Diet rich in fiber, low in refined carbs
- Regular exercise
- Smoking cessation
- Blood pressure control
- Weight management
🛡️ Prevention & Monitoring
- Annual retinal screening
- Regular urine tests for microalbuminuria
- Foot exams for neuropathy
- Blood pressure and lipid control
🧠 Prognosis
- If detected early and managed aggressively, progression can be slowed or even halted
- Poor control can lead to vision loss, kidney failure, and limb amputation