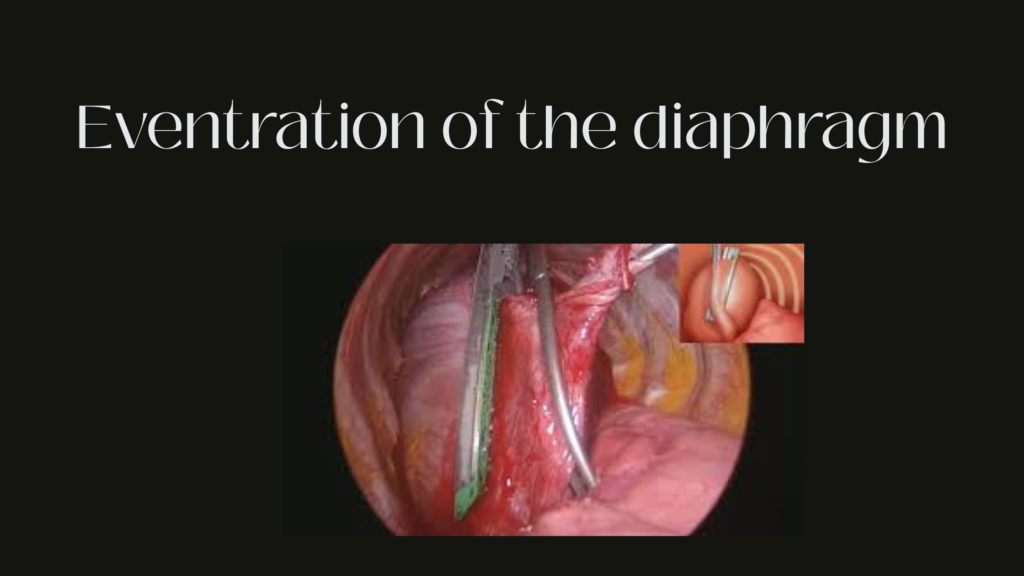
Eventration of the diaphragm
Eventration of the diaphragm is a condition where part or all of the diaphragm is abnormally elevated due to weakness or thinning of the muscle, but the diaphragm remains intact—unlike in hernias, where there is a hole. 🧬 What Is Diaphragmatic Eventration? 🔍 Types 1. Congenital Eventration 2. Acquired Eventration ⚠️ Symptoms 🧒 In Infants/Children: […]