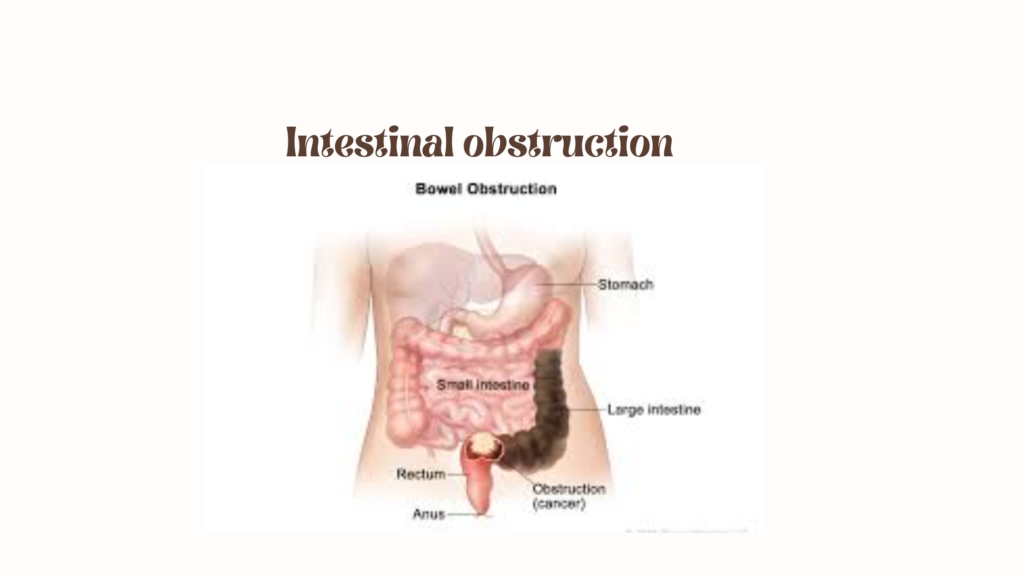
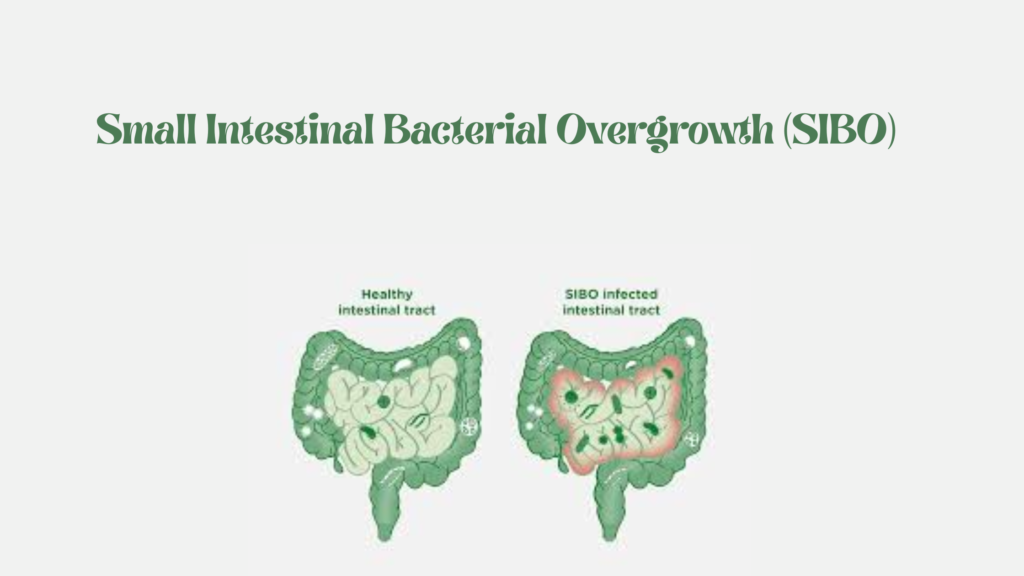
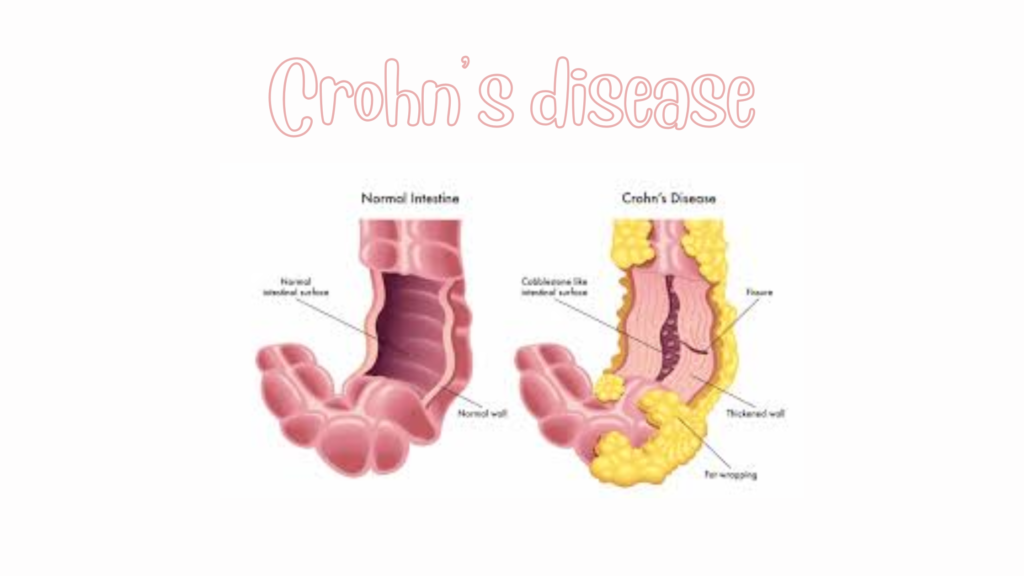
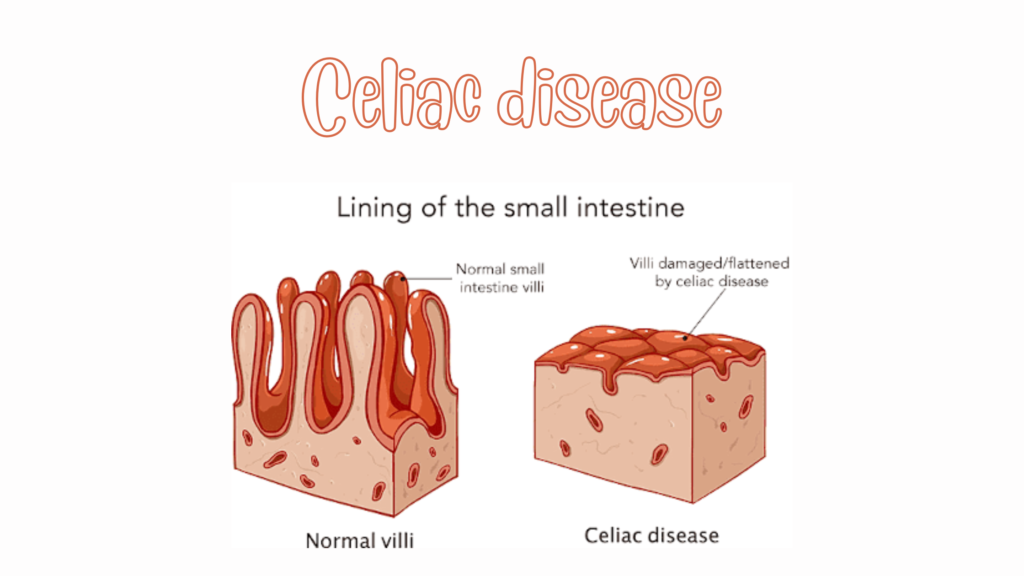
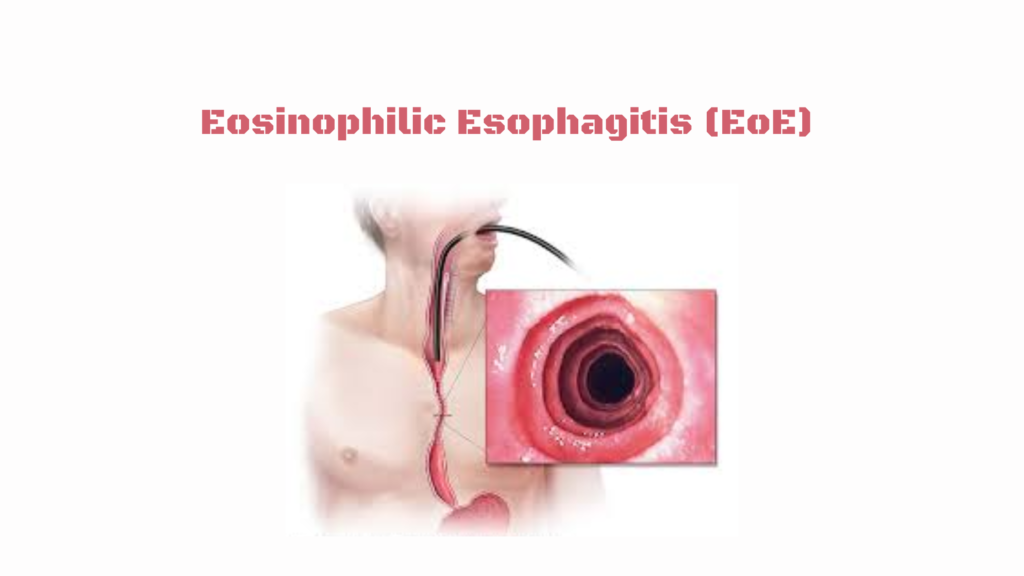
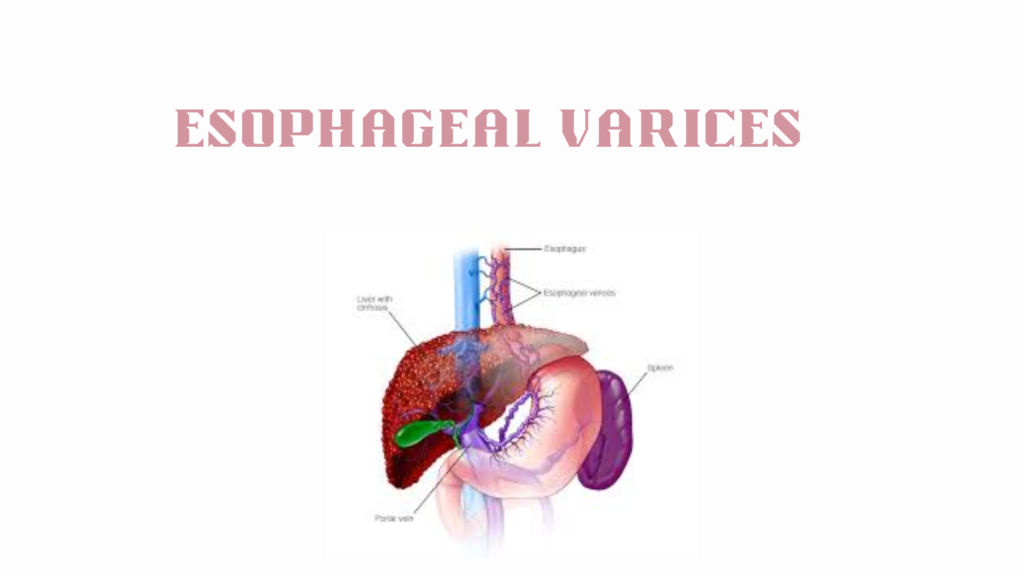
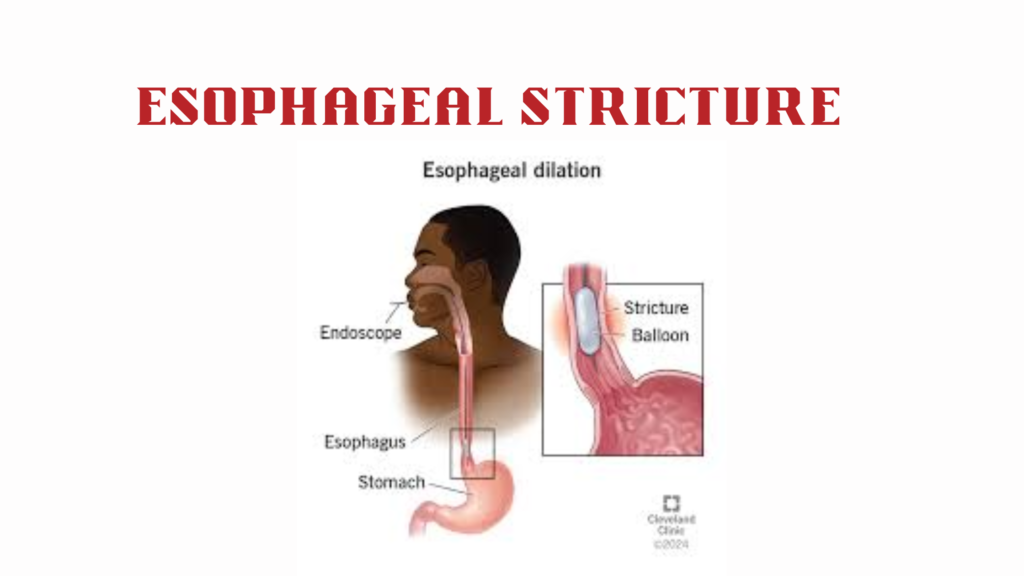
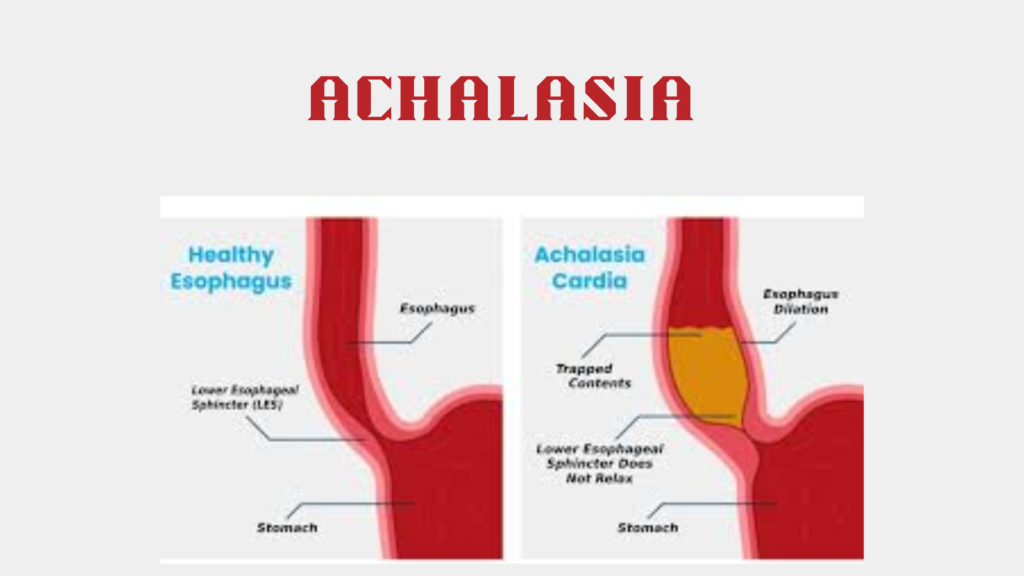
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a blockage that prevents the normal flow of contents through the small or large intestine. It can be partial or complete and may lead to serious complications like bowel ischemia or perforation if untreated. 🧬 Pathophysiology ⚠️ Types of Intestinal Obstruction Type Cause Examples Mechanical Adhesions, hernias, tumors, volvulus, intussusception, strictures Functional […]