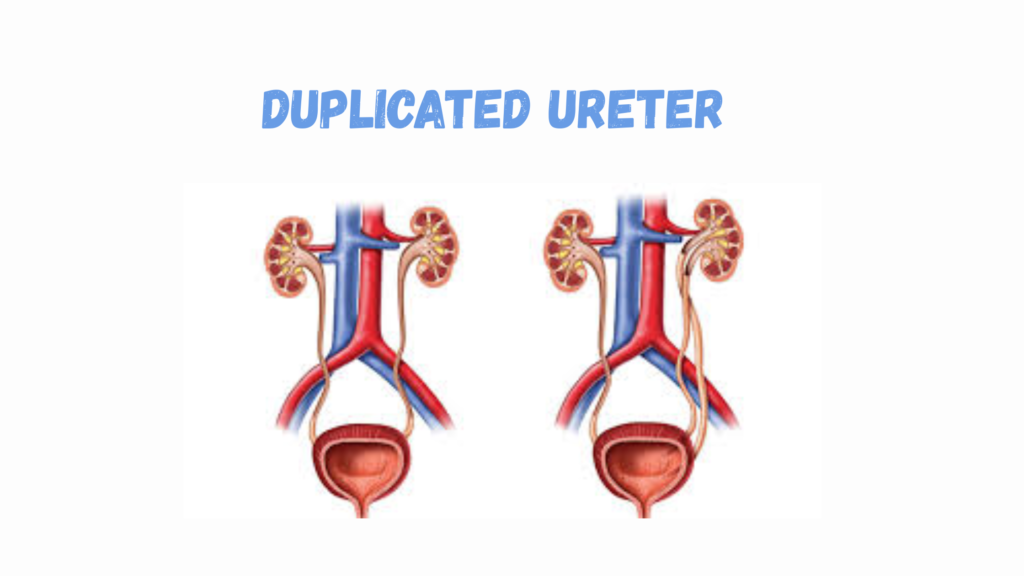
Duplicated Ureter (Duplex Ureter or Ureteral Duplication)
A duplicated ureter is a congenital condition where two ureters drain a single kidney instead of the usual one. It can occur on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral) and may be complete or incomplete.
🧬 Types of Ureteral Duplication
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Complete | Two separate ureters drain from the kidney to the bladder (or other ectopic site) |
| Incomplete | Two ureters start separately but join into one before entering the bladder |
📌 Epidemiology
- Occurs in about 1 in 100–500 live births
- More common in females
- Often found incidentally, but can also cause urinary problems, especially in childhood
⚠️ Clinical Significance
Many people are asymptomatic, but duplication may predispose to:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidney)
- Ureterocele (ballooning of the lower ureter)
- Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) – especially in the lower pole ureter
- Obstruction – especially of the upper pole ureter
- Incontinence – if ectopic ureter inserts outside the bladder (e.g., into the urethra or vagina)
🧪 Diagnosis
1. Ultrasound
- May show hydronephrosis or a ureterocele
2. Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG)
- Used to detect reflux into one or both ureters
3. Magnetic Resonance Urography (MRU) or CT Urogram
- Provides detailed anatomy of the duplication
4. Nuclear Renal Scan (DMSA)
- Assesses differential function between upper and lower poles of the kidney
🩺 Treatment
Treatment depends on symptoms and associated complications:
✅ Asymptomatic
- Observation only with periodic monitoring
⚕️ Symptomatic
May require one or more of the following:
- Antibiotic prophylaxis – to prevent recurrent UTIs
- Surgical correction – if there’s obstruction, reflux, or incontinence:
- Ureteral reimplantation
- Partial nephrectomy – if non-functioning upper pole
- Ureterocele excision
- Ureteroureterostomy – connecting duplicated ureters into one
- Endoscopic management – minimally invasive options for selected cases
🧠 Weigert-Meyer Rule (anatomical pattern in complete duplication)
- Upper pole ureter tends to insert ectopically and is prone to obstruction/ureterocele
- Lower pole ureter inserts in a normal location but is prone to reflux
📈 Prognosis
- Excellent in most cases with appropriate management.
- Early detection and monitoring are key to preventing kidney damage.