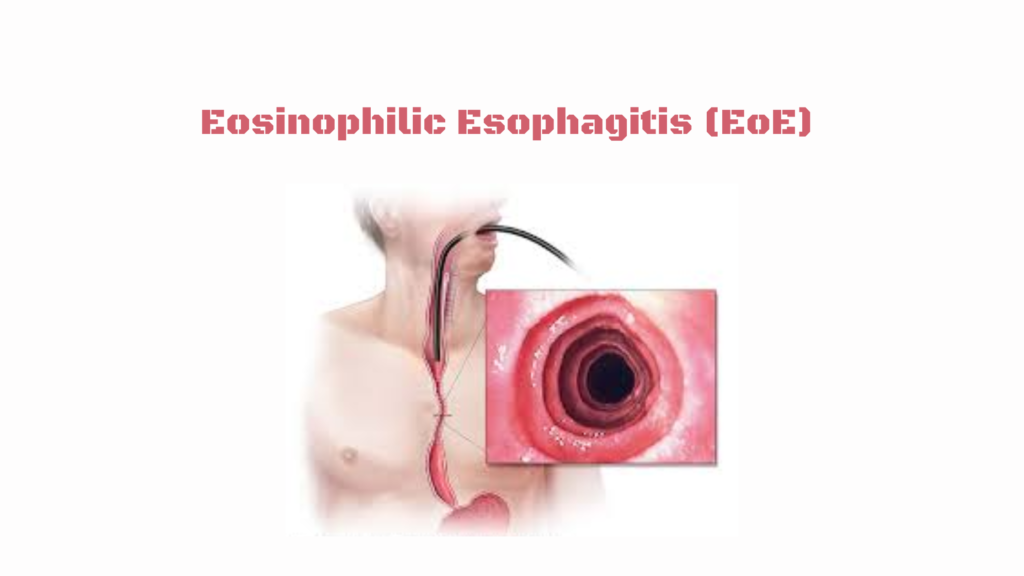
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated disease of the esophagus characterized by inflammation with eosinophils (a type of white blood cell). It leads to difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), food impaction , and long-term esophageal remodeling or narrowing if untreated.
🧬 Pathophysiology Triggered by food allergens or environmental allergens . Leads to recruitment of eosinophils into the esophageal lining. Chronic inflammation → fibrosis, strictures, and motility problems . Unlike GERD, acid suppression alone does not resolve the inflammation. ⚠️ Risk Factors Male sex (up to 3:1 ratio)Age : common in children and young adultsAtopic history : asthma, eczema, allergic rhinitis, food allergiesFamily history of EoE or other allergic disorders😖 Symptoms In Adults In Children 🥴 Dysphagia (solids) Feeding difficulties 🍗 Food impaction Vomiting or regurgitation 📉 Chest pain Failure to thrive 🔁 Reflux not responsive to PPIs Abdominal pain 🥤 Slow, cautious eating habits Avoidance of textured foods
🧪 Diagnosis ✅ Upper Endoscopy (EGD) with Biopsies Normal-appearing mucosa is possible, so biopsy is essential Common findings:Furrows White plaques or exudates Rings or trachealization Strictures or narrow-caliber esophagus 🔬 Histology ≥ 15 eosinophils per high-power field (HPF) Biopsies from multiple levels of the esophagus 🧪 Rule Out Other Causes GERD (may coexist) Achalasia, infections, drug-induced esophagitis 💊 Treatment Options 1. Dietary Therapy ✔ Effective, especially in children
Approach Details Six-food elimination diet (SFED) Avoids milk, soy, eggs, wheat, nuts, seafood Elemental diet Amino-acid based formula; very effective but hard to maintain Targeted elimination Based on allergy testing (limited accuracy)
2. Topical Steroids (Swallowed) Fluticasone (swallowed, not inhaled) or budesonide slurry Reduce eosinophilic inflammation Rinse mouth after to prevent oral thrush 3. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) Help some patients (PPI-responsive EoE ) Also reduce inflammation and may alter esophageal barrier function 4. Biologics Dupilumab (anti–IL-4/IL-13 monoclonal antibody)Approved for moderate-to-severe EoE not controlled by diet or steroids 5. Esophageal Dilation For strictures or food impaction Risk of perforation is low with proper technique 📊 Monitoring & Follow-Up Repeat endoscopy with biopsy after 8–12 weeks of treatment to assess responseSymptom improvement does not always equal histologic remission Long-term monitoring often required 📉 Complications if Untreated Esophageal strictures Food impaction (ER visits common)Feeding difficulties in childrenEsophageal remodeling and fibrosis🔄 EoE vs GERD vs Achalasia Feature EoE GERD Achalasia Cause Immune-mediated (allergens) Acid reflux Motility disorder Dysphagia Intermittent, solid foods Occasional, if stricture present Both solids and liquids Heartburn Rare Common Rare Endoscopy Rings, furrows, plaques Erosions, ulcers, hiatal hernia Dilated esophagus, tight LES Treatment Diet, steroids, biologics PPIs, lifestyle Myotomy, dilation, POEM