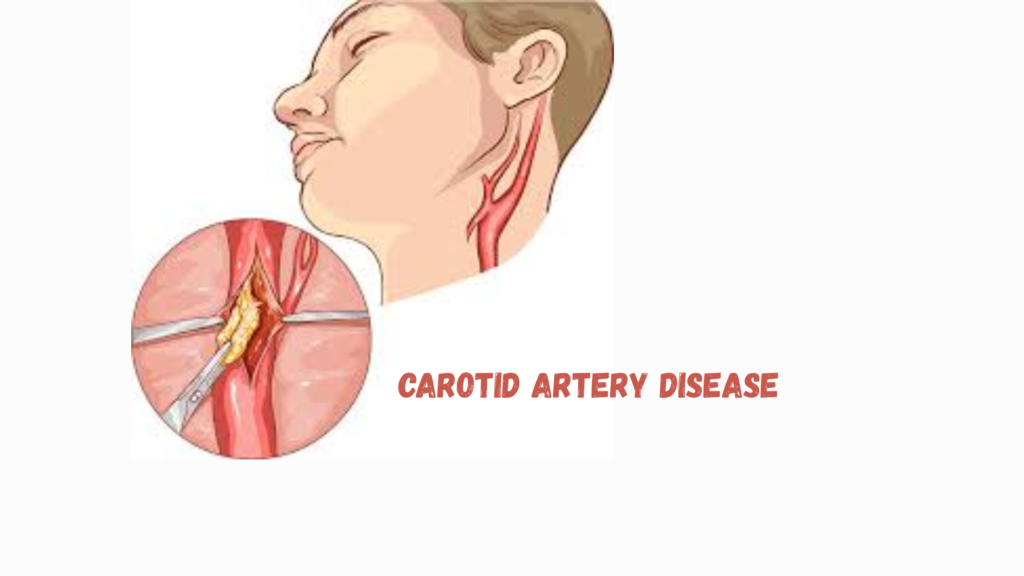
Carotid Artery Disease is a serious condition where the carotid arteries, located on each side of the neck, become narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup).
🧠 What Are Carotid Arteries?
- They supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain.
- There are two carotid arteries: left and right.
- Narrowing of these arteries increases the risk of stroke.
⚠️ What Is Carotid Artery Disease?
- It’s a form of vascular disease caused by:
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup)
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Age and family history
🩺 Symptoms
Often no symptoms until a stroke or mini-stroke (TIA) occurs.
Signs of TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) — “Warning Stroke”:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in face, arm, or leg (usually on one side)
- Trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden loss of vision in one eye
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Symptoms usually last minutes to hours and then go away — but it’s a medical emergency
🧪 Diagnosis
- Carotid ultrasound (non-invasive)
- CT angiography (CTA) or MR angiography (MRA)
- Carotid angiogram (invasive, most accurate)
💊 Treatment Options
🩹 Lifestyle Changes:
- Quit smoking
- Eat a low-fat, heart-healthy diet
- Exercise regularly
- Manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
💊 Medications:
- Antiplatelets (e.g., aspirin) – prevent blood clots
- Statins – lower cholesterol
- Blood pressure medications
🛠️ Procedures:
- Carotid Endarterectomy
- Surgical removal of plaque from the artery.
- Often recommended if 50–70%+ blockage with symptoms.
- Carotid Artery Stenting
- A catheter places a stent to open the artery.
- Less invasive; often for patients at higher surgical risk.
🚨 Complications if Untreated
- Stroke
- Permanent brain damage
- Death
✅ Prevention
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol
- Avoid tobacco
- Eat a healthy diet (Mediterranean or DASH)
- Exercise (at least 150 min/week)
- Manage stress