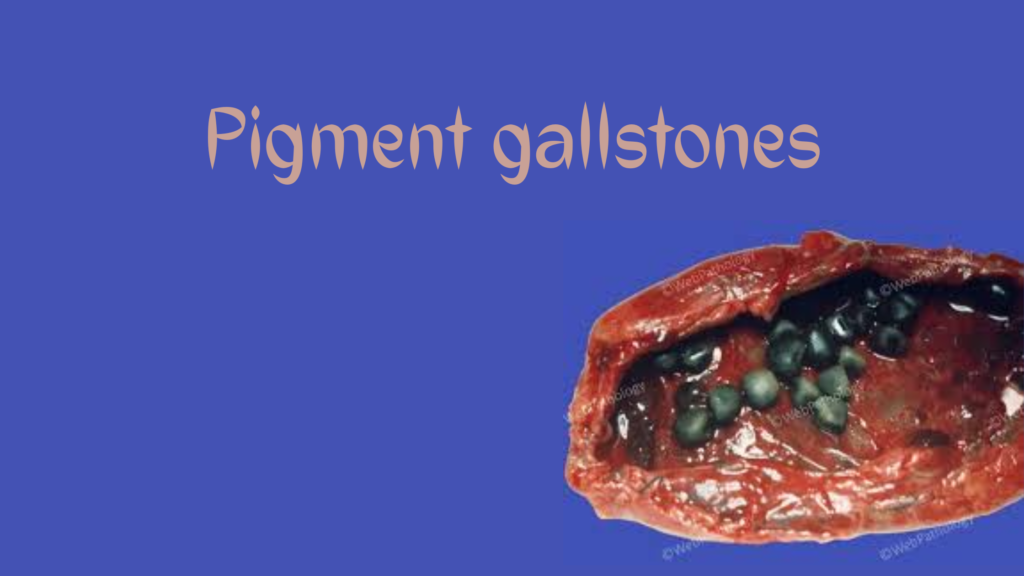
Pigment gallstones are a type of gallstone that form when there is an excess of bilirubin in the bile. Bilirubin is a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. These stones are darker in color compared to cholesterol stones and are less common, accounting for about 20–25% of all gallstones in the United States. (news-medical.net, webpathology.com)
🟣 Types of Pigment Gallstones
- Black Pigment Gallstones:
- Composition: Primarily made of calcium bilirubinate and inorganic calcium salts.
- Formation: Develop in sterile bile, often due to conditions that increase red blood cell turnover.
- Associated Conditions: Chronic hemolytic anemia, cirrhosis, and alcoholic liver disease.
- Location: Commonly found in the gallbladder.(msdmanuals.com, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, abdominalkey.com)
- Brown Pigment Gallstones:
- Composition: Contain calcium bilirubinate, cholesterol, and fatty acids.
- Formation: Form in infected bile ducts, often due to bacterial infections or parasitic infestations.
- Associated Conditions: Biliary tract infections, biliary stasis, and parasitic infections like liver flukes.
- Location: Frequently found in the bile ducts rather than the gallbladder.(wjgnet.com, emedicine.medscape.com)
⚠️ Risk Factors
- Black Pigment Stones:
- Chronic hemolytic conditions (e.g., sickle cell anemia, hereditary spherocytosis).
- Liver cirrhosis.
- Chronic alcoholism.
- Advanced age.(emedicine.medscape.com, abdominalkey.com, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Brown Pigment Stones:
- Biliary tract infections.
- Biliary stasis (e.g., due to strictures or choledochal cysts).
- Parasitic infections (e.g., liver flukes).
- Chronic pancreatitis.(abdominalkey.com)
🩺 Symptoms
Pigment gallstones may be asymptomatic or cause symptoms when they obstruct bile flow. Common symptoms include:
- Severe abdominal pain, especially in the upper right quadrant.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Fever and chills (if infection is present).(health.com)
🧪 Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Ultrasound: The primary imaging tool for detecting gallstones.
- CT Scan or MRI: Used in complex cases or when complications are suspected.
- Blood Tests: To assess liver function and detect signs of infection or inflammation.(verywellhealth.com)
🛠️ Treatment Options
- Black Pigment Stones:
- Cholecystectomy (surgical removal of the gallbladder) is often curative.
- Management of underlying conditions (e.g., hemolytic anemia, cirrhosis) is essential.
- Brown Pigment Stones:
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to remove stones from bile ducts.
- Cholecystectomy if the gallbladder is involved.
- Treatment of underlying infections or parasitic infestations.(health.com, msdmanuals.com)
🛡️ Prevention Strategies
- For Black Pigment Stones:
- Management of hemolytic conditions.
- Regular monitoring and treatment of liver diseases.
- For Brown Pigment Stones:
- Prompt treatment of biliary tract infections.
- Surgical correction of biliary tract abnormalities.
- Prevention and treatment of parasitic infections.(verywellhealth.com)